- MORPHOICΞS
- Posts
- 🌌 Steal My 8-Step AI Workflow for Course Creators.
🌌 Steal My 8-Step AI Workflow for Course Creators.
Everything from idea to sales page—plug, play, and launch without the guesswork.

From Idea to Income in 1 Weekend? This AI Workflow Says Yes🌌
— Build your course faster, market smarter, and skip the burnout—here’s your step-by-step shortcut.
Estimated Reading Time: 6 minutes. — Wednesday, June 4th , 2025.
Hello again, Morphoices!

Creating and launching a course isn’t just one job—it’s twenty. From idea validation to scripting, lead magnets, sales copy, and content promotion, the process can feel like trying to juggle in a wind tunnel.
This week in Tools of the Trade, you’re getting a full-stack AI workflow that takes you from blank doc to launch-ready course.
No VA, no tech overload—just smart prompts, strategic moves, and a repeatable system that saves you serious time.

Let’s map it out!


Today’s Tool: AI-Powered Course Creation Workflow
Tool Type: Workflow Automation + Prompt System.
Main Benefit: Build and launch an entire course faster—with clarity, not chaos.

The Workflow: 8 Steps to Go From Idea to Income
You can run each step inside ChatGPT or your AI tool of choice. Just copy, paste, and plug in your course topic.

Step 1: Find a Profitable Idea
Title of the Prompt:
"Generate Profitable Online Course Topics with Demand Validation for [Insert Niche]"
Purpose of the Prompt:
The purpose is to generate five profitable, audience-focused online course topic ideas for a specified niche, addressing real pain points with clear solutions and demand validation metrics. It ensures course creators can quickly identify marketable topics and validate them for profitability.
IA Prompt:
Structured AI Prompt: Brainstorm Compelling Online Course Topics
1. Set the Scene: Define the AI’s Role
Act as an expert instructional designer and market researcher specializing in online education and [insert niche]. Your task is to assist with brainstorming profitable online course topics that address specific audience pain points, ensuring responses are tailored to [specific audience, e.g., solopreneurs, professionals, or hobbyists] seeking practical solutions in [insert niche].
Customization Options: Allow users to specify the niche (e.g., productivity, digital marketing, personal finance) and audience demographics (e.g., age, experience level).
Constraint for Authenticity: Focus on real-world challenges faced by the audience, such as limited time, budget, or technical skills, to ensure relevance.
2. Define the Goal: Specify Output and Format
Your task is to generate five compelling online course topic ideas that solve specific pain points in [insert niche]. The output should be a structured list with detailed descriptions, designed to achieve high audience engagement and market demand validation within 30 days.
SMART Goal Integration: The topics must be specific to the niche, measurable through demand indicators (e.g., search trends, competitor analysis), achievable within the audience’s skill level, relevant to their goals, and time-bound for rapid validation.
Performance Target: Each topic must include a pain point, a proposed solution, and one demand validation metric (e.g., keyword search volume or social media engagement).
3. Provide a Clear Structure
Structure the response as follows:
Overview: A brief introduction to the niche and its audience needs.
Course Topic List: Five course topic ideas, each with:
Topic Title: A concise, marketable title.
Pain Point: The specific audience challenge addressed.
Solution: How the course solves the pain point.
Validation Metric: A measurable indicator of demand (e.g., search volume, trending hashtags).
Next Steps: Recommendations for validating and prioritizing topics (e.g., surveys, keyword research).
Enhanced Formatting for Precision: Use a table to summarize the five topics for clarity.
Visual Aids Suggestion: Include a flowchart for the topic validation process (e.g., “Research → Survey → Prototype”).
4. Specify the Tone and Audience
Write in a professional yet engaging tone suited for [specific audience, e.g., course creators or entrepreneurs] with intermediate knowledge of [insert niche]. Use clear, industry-specific phrasing to convey authority and build trust.
Tone Variations:
For course creators: Emphasize actionable insights and market potential.
For niche experts: Highlight technical depth and audience alignment.
Industry Adaptation: Ensure language aligns with the niche’s expectations (e.g., “growth hacking” for marketing, “wellness” for health).
5. Set Constraints and Guidelines
Ensure the response includes five unique course topics, avoids generic or oversaturated ideas (e.g., “How to Make Money Online”), and remains within 300 words total, with each topic description under 50 words. Optimize for readability with sentences under 20 words. Avoid jargon unless niche-specific and necessary for precision.
6. Include Examples for Benchmarking
Follow this example:
Topic Title: “Time Management Mastery for Remote Workers”
Pain Point: Remote workers struggle to balance tasks and avoid burnout.
Solution: Teach prioritization frameworks and productivity tools for efficiency.
Validation Metric: 10,000 monthly searches for “remote work productivity.”
Custom Length Variations:
Short Version (100 words): Summarize five topics with pain points.
Detailed Version (300 words): Include validation metrics and next steps.
7. Refine for Quality
Before finalizing, review for market relevance, audience alignment, and actionability. Refine by strengthening topic specificity and ensuring each solution is practical.
Self-Assessment Checklist:
Does the response address niche-specific pain points?
Is the language clear and engaging for the target audience?
Are validation metrics included for all topics?
8. Scenario-Based Variations
Adapt the prompt for specific niches:
Marketing: “Generate course topics for a social media campaign targeting [specific platform, e.g., Instagram].”
Education: “Develop course ideas for [specific audience, e.g., K-12 teachers] learning [specific skill, e.g., edtech integration].”
Problem-Solving: “Identify course topics addressing [specific challenge, e.g., financial literacy for young adults].”
9. AI Optimization Techniques
Chaining Prompts: First, analyze audience pain points in [insert niche]. Then, propose course topics. Finally, suggest validation methods.
Iterative Feedback Loops: Revise topics based on user feedback to emphasize high-demand ideas.
10. Embedded Worksheets and Tools
Provide a downloadable template for users to input niche and audience details. Include an AI Output Tracker to compare topic demand metrics across multiple iterations.
Additional Premium Enhancements
Customization Options: Users can specify niche (e.g., “personal finance for millennials”), audience (e.g., beginners, advanced), or platform (e.g., Udemy, Teachable).
Advanced Variations: Modify for niche subcategories (e.g., “Instagram marketing for e-commerce” vs. “content marketing for bloggers”).
Visual/Structural Guides: Suggest a table summarizing topics and a flowchart for validation steps (e.g., “Keyword Research → Audience Survey → Topic Selection”).
Notes
Placeholders (e.g., [insert niche], [specific audience]) ensure versatility across use cases.
The prompt is designed for advanced users, balancing conciseness with depth for a €600 guide.
The output is reviewed for logical flow, niche relevance, and actionable insights.
Please let me know if you’d like me to refine this further or create another prompt for a different guide topic!
Prompt Template Usage Guide.
Placeholders Explained
[insert niche]
Defines the specific subject area the course will address.
Example: digital marketing, personal finance, wellness.[specific audience]
Identifies the target learner group.
Example: solopreneurs, freelance designers, small business owners.[specific platform] (optional)
Specifies where the course will be hosted or promoted.
Example: Udemy, Teachable, LinkedIn Learning.[specific skill / challenge] (optional, used in scenario-based variations)
Focuses on a concrete topic or problem area.
Example: email automation, burnout prevention, budgeting.

What Must Be Changed in the Template
[insert niche] and [specific audience] must be clearly defined. These anchor the AI's focus on solving real problems within a specific market, ensuring relevancy and quality.
The tone and phrasing should be adapted to match industry expectations. For example, use “scaling strategy” for business audiences or “student outcomes” for educators.

Optional Improvements
Add a platform to tailor suggestions to content standards and audience behavior on that site.
Narrow down to a sub-niche or specific pain point to generate more targeted and less saturated topic ideas.
Specify experience level (e.g., beginner, intermediate) for better alignment with course complexity.
Choose between short or detailed output formats depending on the use case (e.g., for pitch decks or full planning).
Apply scenario-based variations to address niche-specific use cases (e.g., “social media for therapists” instead of generic marketing).
Example Output:
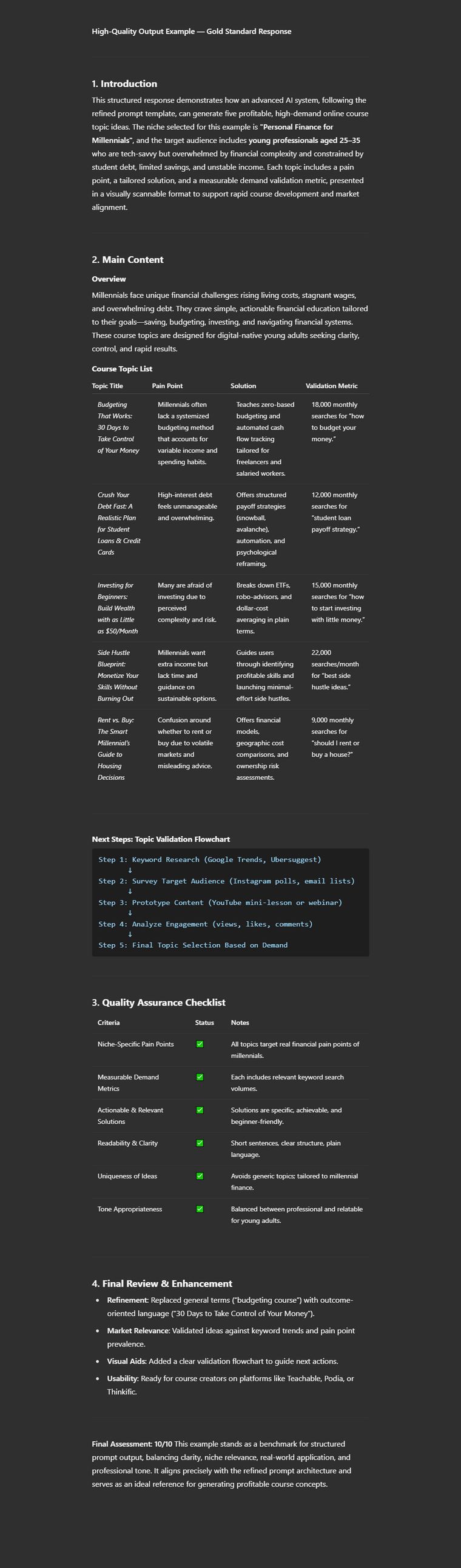

Step 2: Outline the Entire Course
Title of the Prompt:
"Design a Comprehensive Course Outline for [Insert Topic] with Modules and Learning Outcomes"
Purpose of the Prompt:
The purpose is to create a comprehensive, actionable course outline for a specified topic, including modules, lessons, and learning outcomes, tailored to the audience’s needs and designed for effective learning and engagement within a set timeframe.
IA Prompt:
Structured AI Prompt: Create a Comprehensive Course Outline for [Insert Topic]
1. Set the Scene: Define the AI’s Role
Act as an expert curriculum designer and instructional designer specializing in online education and [insert topic]. Your task is to assist with creating a complete course outline tailored to [specific audience, e.g., beginners, professionals, or hobbyists] in [insert topic], addressing their learning needs and preferences.
Customization Options: Allow users to specify the topic (e.g., digital marketing, yoga, data analysis), audience level (e.g., beginner, intermediate), and delivery platform (e.g., Udemy, corporate training).
Constraint for Authenticity: Focus on real-world challenges faced by the audience, such as limited prior knowledge, time constraints, or need for practical skills.
2. Define the Goal: Specify Output and Format
Your task is to create a detailed course outline for a course on [insert topic]. The output should be a structured document including module titles, lesson breakdowns, and learning outcomes, designed to achieve learner proficiency and engagement within [insert timeframe, e.g., 6 weeks].
SMART Goal Integration: The outline must be specific to the topic, measurable through defined learning outcomes, achievable within the audience’s skill level, relevant to their goals, and time-bound for course completion.
Performance Target: Include at least 4–6 modules, each with 2–4 lessons, and clear, actionable learning outcomes for each lesson.
3. Provide a Clear Structure
Structure the response as follows:
Course Overview: Summarize the course purpose, target audience, and overall learning objectives.
Module Breakdown: List 4–6 modules, each including:
Module Title: A concise, descriptive title.
Lesson Titles: 2–4 lessons per module with brief descriptions.
Learning Outcomes: Specific skills or knowledge gained per lesson.
Assessment and Engagement: Suggest methods to evaluate learner progress (e.g., quizzes, projects) and engagement tactics (e.g., discussions, activities).
Course Timeline: Provide a suggested week-by-week schedule for delivery.
Enhanced Formatting for Precision: Use a table to summarize modules, lessons, and outcomes for clarity.
Visual Aids Suggestion: Include a course progression flowchart or timeline diagram to visualize the learning journey.
4. Specify the Tone and Audience
Write in a professional yet approachable tone suited for [specific audience, e.g., course creators or educators] with intermediate knowledge of [insert topic]. Use clear, industry-specific phrasing to ensure relevance and credibility.
Tone Variations:
For educators: Emphasize pedagogical rigor and learner engagement.
For course creators: Focus on marketability and practical implementation.
Industry Adaptation: Align language with the topic’s context (e.g., “optimization” for tech, “wellness” for health).
5. Set Constraints and Guidelines
Ensure the response includes 4–6 modules, avoids overly broad or generic lesson titles (e.g., “Introduction to Topic”), and remains within 400 words total, with each module description under 100 words. Optimize for readability with sentences under 20 words. Avoid jargon unless essential for the topic.
6. Include Examples for Benchmarking
Follow this example:
Module Title: “Foundations of Digital Marketing”
Lesson Titles:
Lesson 1: Understanding Digital Channels (Overview of SEO, social media, and PPC).
Lesson 2: Setting Campaign Goals (Defining SMART objectives for campaigns).
Learning Outcomes:
Lesson 1: Identify three key digital marketing channels.
Lesson 2: Create a SMART goal for a sample campaign.
Custom Length Variations:
Short Version (150 words): Summarize modules and key outcomes.
Detailed Version (400 words): Include lesson descriptions, outcomes, and engagement tactics.
7. Refine for Quality
Before finalizing, review for alignment with learner needs, logical progression, and actionability. Refine by ensuring each module builds on the previous one and outcomes are measurable.
Self-Assessment Checklist:
Does the outline address the topic’s learning objectives?
Is the structure clear and engaging for the audience?
Are all modules and outcomes specific and actionable?
8. Scenario-Based Variations
Adapt the prompt for specific contexts:
Marketing: “Create a course outline for a social media marketing course targeting [specific audience, e.g., small businesses].”
Education: “Develop a course outline for [specific topic, e.g., STEM] for [specific audience, e.g., high school students].”
Professional Development: “Design a course outline for [specific skill, e.g., leadership] for [specific audience, e.g., mid-level managers].”
9. AI Optimization Techniques
Chaining Prompts: First, identify audience needs for [insert topic]. Then, structure modules and lessons. Finally, define measurable outcomes.
Iterative Feedback Loops: Revise the outline based on user feedback to emphasize high-impact lessons or engagement tactics.
10. Embedded Worksheets and Tools
Provide a downloadable template for users to input topic, audience, and platform details. Include an AI Output Tracker to compare outline iterations for depth and engagement.
Additional Premium Enhancements
Customization Options: Users can specify topic (e.g., “Python programming”), audience (e.g., beginners), and course duration (e.g., 4 weeks).
Advanced Variations: Modify for specific platforms (e.g., “outline for a self-paced Udemy course” vs. “live corporate training”).
Visual/Structural Guides: Suggest a table summarizing modules and a flowchart for course progression (e.g., “Module 1 → Module 2 → Final Project”).
Notes
Placeholders (e.g., [insert topic], [specific audience]) ensure versatility across use cases.
The prompt is designed for advanced users, balancing conciseness with depth for a €600 guide.
The output is reviewed for logical flow, audience alignment, and actionable outcomes.
Please let me know if you’d like me to refine this further or create another prompt for a different guide topic!
Prompt Template Usage Guide.
Placeholders Explained
[insert topic]
Defines the main subject of the course.
Example: data analysis, yoga, branding strategy.[specific audience]
Identifies the learners the course is designed for.
Example: beginners, corporate teams, freelance designers.[insert timeframe]
Sets the total duration for the course.
Example: 4 weeks, 6 weeks, 2 months.[delivery platform] (optional)
Indicates where the course will be delivered or published.
Example: Udemy, Thinkific, internal LMS.[specific skill / context] (optional in scenario-based variations)
Narrows the focus or learning environment.
Example: leadership for remote teams, mindfulness for busy professionals.

What Must Be Changed in the Template
[insert topic] and [specific audience] must always be customized. These define the entire instructional strategy and ensure relevance to the learners.
The timeframe should match audience availability and content depth. Without this, the pacing and scope may be misaligned.
Language and tone should reflect the audience's knowledge level and industry (e.g., avoid overly technical terms for beginners).

Optional Improvements
Add a delivery platform to tailor the format and structure (e.g., self-paced vs. instructor-led).
Specify a real-world challenge or practical need to sharpen the course focus.
Indicate a learning format preference (e.g., video-heavy, interactive, project-based) to refine module suggestions.
Choose between short or detailed output versions depending on your use case (high-level planning or ready-to-publish structure).
Use scenario-based variations for more niche-aligned outputs (e.g., technical skills for nonprofits, wellness training for HR teams).
Example Output:


Step 3: Write the Lessons (Faster Than Ever)
Title of the Prompt:
"Write an Actionable Lesson Script for [Lesson Title] in [Insert Topic]"
Purpose of the Prompt:
The purpose is to generate a detailed, actionable lesson script for a specified lesson within a course on a given topic, ensuring learner engagement, clear instruction, and practical application through structured content, examples, and exercises.
IA Prompt:
Structured AI Prompt: Write a Detailed Lesson Script for [Lesson Title] in [Insert Topic]
1. Set the Scene: Define the AI’s Role
Act as an expert instructional designer and content creator specializing in online education and [insert topic]. Your task is to assist with writing a detailed lesson script for “[Lesson Title]” from a course on [insert topic], tailored to [specific audience, e.g., beginners, professionals, or hobbyists] seeking practical, actionable knowledge.
Customization Options: Allow users to specify the topic (e.g., personal finance, web development), lesson title, audience level (e.g., beginner, advanced), and delivery format (e.g., video, text, interactive).
Constraint for Authenticity: Address audience challenges, such as limited prior knowledge, time constraints, or need for practical application, to ensure relevance and engagement.
2. Define the Goal: Specify Output and Format
Your task is to write a detailed lesson script for “[Lesson Title]” from a course on [insert topic]. The output should be a structured script (text format), designed to achieve learner comprehension and skill application within a 15–30 minute lesson.
SMART Goal Integration: The script must be specific to the lesson’s objectives, measurable through learner actions (e.g., completing an exercise), achievable within the audience’s skill level, relevant to the course goals, and time-bound for a single lesson.
Performance Target: Include an introduction, main content with actionable steps, examples, and a summary with key takeaways.
3. Provide a Clear Structure
Structure the response as follows:
Lesson Introduction: Outline the lesson’s purpose, objectives, and relevance to the audience (50–100 words).
Main Content: Break into 3–5 segments, each covering a key concept or step, with actionable instructions and examples (200–300 words total).
Practical Exercise: Provide a hands-on activity or task to reinforce learning (50–100 words).
Summary and Takeaways: Recap key points and suggest next steps (50 words).
Enhanced Formatting for Precision: Use bullet points for main content segments and a table to summarize key concepts and examples.
Visual Aids Suggestion: Include a diagram or flowchart to illustrate the lesson’s process or concept (e.g., a decision tree for problem-solving lessons).
4. Specify the Tone and Audience
Write in a friendly, clear, and engaging tone suited for [specific audience, e.g., course creators or learners] with beginner to intermediate knowledge of [insert topic]. Use industry-specific phrasing where necessary to ensure credibility and relatability.
Tone Variations:
For learners: Maintain a conversational, supportive tone to encourage engagement.
For course creators: Emphasize script clarity and teachability for easy adaptation.
Industry Adaptation: Align language with the topic’s context (e.g., “optimization strategies” for tech, “mindfulness techniques” for wellness).
5. Set Constraints and Guidelines
Ensure the response includes actionable steps, at least two relevant examples, and avoids generic content (e.g., “be motivated”). Keep the script within 400–500 words, with sentences under 20 words for clarity. Avoid jargon unless essential for the topic and defined for the audience.
6. Include Examples for Benchmarking
Follow this example:
Lesson Title: “Crafting Effective Email Subject Lines”
Introduction: Explain why subject lines matter for email open rates.
Main Content Segment:
Concept: Use action-oriented language.
Example: “Boost Your Sales Today!” vs. “Newsletter #5.”
Practical Exercise: Write three subject lines for a sample campaign.
Summary: Recap the importance of concise, action-driven subject lines.
Custom Length Variations:
Short Version (200 words): Focus on introduction, key concepts, and summary.
Detailed Version (500 words): Include detailed segments, examples, and exercise.
7. Refine for Quality
Before finalizing, review for learner engagement, logical flow, and actionability. Refine by ensuring examples are relevant and the exercise aligns with the lesson’s objectives.
Self-Assessment Checklist:
Does the script meet the lesson’s learning objectives?
Is the tone engaging and clear for the audience?
Are actionable steps and examples included?
8. Scenario-Based Variations
Adapt the prompt for specific contexts:
Marketing: “Write a script for a lesson on [specific tactic, e.g., creating Instagram ads] for [specific audience, e.g., small businesses].”
Education: “Develop a script for a lesson on [specific topic, e.g., algebra basics] for [specific audience, e.g., high school students].”
Professional Development: “Create a script for a lesson on [specific skill, e.g., time management] for [specific audience, e.g., corporate employees].”
9. AI Optimization Techniques
Chaining Prompts: First, define the lesson’s objectives. Then, outline key concepts and examples. Finally, craft the exercise and summary.
Iterative Feedback Loops: Revise the script based on user feedback to enhance clarity or engagement.
10. Embedded Worksheets and Tools
Provide a downloadable lesson script template for users to input topic, lesson title, and audience details. Include an AI Output Tracker to compare script iterations for engagement and clarity.
Additional Premium Enhancements
Customization Options: Users can specify lesson title (e.g., “Introduction to SEO”), topic (e.g., digital marketing), audience (e.g., freelancers), and format (e.g., video script).
Advanced Variations: Modify for delivery methods (e.g., “script for a live workshop” vs. “self-paced e-learning module”).
Visual/Structural Guides: Suggest a table summarizing concepts and a flowchart for the lesson’s structure (e.g., “Introduction → Concept 1 → Exercise → Summary”).
Notes
Placeholders (e.g., [insert topic], [Lesson Title]) ensure versatility across use cases.
The prompt is designed for advanced users, balancing conciseness with depth for a €600 guide.
The output is reviewed for logical flow, audience engagement, and actionable content.
Please let me know if you’d like me to refine this further or create another prompt for a different guide topic!
Prompt Template Usage Guide.
Placeholders to Customize
Placeholder | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Specific focus of the lesson | “Writing High-Converting Ads” |
| The broader subject area | “Digital Marketing” |
| Intended learner group | “freelance designers” |
| Format of delivery (optional) | “interactive e-learning” |

What Must Be Customized
[Lesson Title] and [Insert Topic] are mandatory — they guide the content depth and focus.
[specific audience] is crucial to ensure tone, pacing, and relevance.
If the script is for a (e.g., video or workshop), include that to influence style and interaction design.
Example Output:


Bonus Move: Systemize It
Once you’ve used this once, turn it into a template. Every new course you build gets faster, smoother, and easier to delegate—or automate.

Mini Review: Is This Worth It?
Pros:
Saves 20–40+ hours per course.
Gives clarity from start to finish.
Removes the “where do I start?” block.
Cons:
Still requires you to bring the spark.
Final Verdict:
For solopreneurs serious about scaling, this is your plug-and-play system. Use it to launch smarter, write faster, and reclaim your time.

Top 5 Industry Headlines to Watch
Notion Adds AI Course Templates — Build your outline where you work.
Kajabi Introduces AI Content Assistant — Instant help with landing pages.
Meta Launches AI Ad Generator — Save time on your promo strategy.
Podia Adds GPT Quiz Builder — Personalize your course experience.
AI Course Creators Cross $10M+ Milestones — Proof that lean teams can scale big.

Takeaway Toolkit
Start with demand-first validation.
Use AI as your backend team for scripting, marketing, and planning.
Save this workflow—then reuse it every time.


Until next time, simplify smart and build bold.
— Valentine.
Morphoices: The Solopreneur’s Guide to Online Course Creation.

P. S. — I may be the one writing, but this newsletter is ours. What direction would you like to see it take? What’s missing that could make it great for you?
Reply